Acupuncture for Smoking Cessation
How nervous system regulation supports craving reduction, stress resilience, and long-term relapse prevention
If you’ve tried to quit smoking before, you already know the hardest part isn’t the decision—it’s what happens afterward. Cravings surge. Stress tolerance drops. Sleep and mood unravel. And despite strong motivation, relapse often follows.
This pattern isn’t a failure of discipline. It reflects how nicotine reshapes the nervous system, stress response, and reward circuitry over time. For many people, lasting smoking cessation requires physiological regulation, not just behavioral restraint.
Acupuncture supports smoking cessation by helping recalibrate the stress–reward loop that sustains nicotine dependence, reducing relapse risk while supporting emotional and nervous system stability (1).
This article explains how acupuncture supports smoking cessation by regulating the nervous system, reducing stress-driven cravings, and interrupting the stress–reward loop that makes nicotine addiction so difficult to break.
Why Smoking Cessation Is a Nervous System Problem, Not a Willpower Problem
Nicotine exerts its addictive pull by rapidly stimulating dopamine and serotonin release, while simultaneously dampening stress perception through the autonomic nervous system (2). Over time, the brain adapts to this artificial regulation.
When nicotine is removed:
Dopamine signaling drops
Stress reactivity increases
Emotional regulation becomes unstable
Habitual coping pathways activate automatically
This is why cravings often peak during stress, fatigue, emotional discomfort, or routine triggers—long after the physical withdrawal phase has passed (3).
From a clinical perspective, smoking becomes a learned nervous system regulation strategy. Until that pattern is addressed, relapse remains likely.
How Acupuncture Influences the Stress–Reward Loop Involved in Nicotine Addiction
Acupuncture works by engaging multiple regulatory pathways simultaneously, rather than targeting a single symptom.
Research shows acupuncture can:
Modulate dopamine and serotonin signaling
Reduce sympathetic (“fight-or-flight”) dominance
Enhance parasympathetic recovery
Improve stress tolerance and emotional regulation
Influence habit-driven neural circuits (4,5)
Rather than suppressing cravings directly, acupuncture helps restore baseline nervous system balance, making cravings less intense, less frequent, and easier to tolerate without acting on them.
→ Acupuncture & Nervous System Regulation
Why Cravings Persist After Nicotine Withdrawal Ends
Many people are surprised when cravings return weeks—or even months—after quitting. This occurs because withdrawal chemistry resolves faster than neural habit loops.
Nicotine becomes paired with:
Stress relief
Focus and stimulation
Emotional numbing
Routine transitions
These associations live in the nervous system, not conscious thought. Acupuncture helps interrupt these loops by reducing baseline stress load and improving regulatory capacity, making it easier to experience discomfort without defaulting to smoking (6).
How Acupuncture Supports Smoking Cessation at the Physiological Level
Neurochemical Stabilization
Acupuncture influences neurotransmitters involved in reward, motivation, and emotional regulation, helping smooth the abrupt neurochemical shifts that accompany cessation (7).
Stress Response Downregulation
Stress is the most common relapse trigger. Acupuncture reduces sympathetic overactivation and improves parasympathetic tone, increasing resilience during high-risk moments (8).
Sensory and Behavioral Effects
Some individuals report reduced enjoyment of cigarettes, altered taste perception, or aversion to smoke. These effects have been documented in clinical studies and may reduce behavioral reinforcement (9).
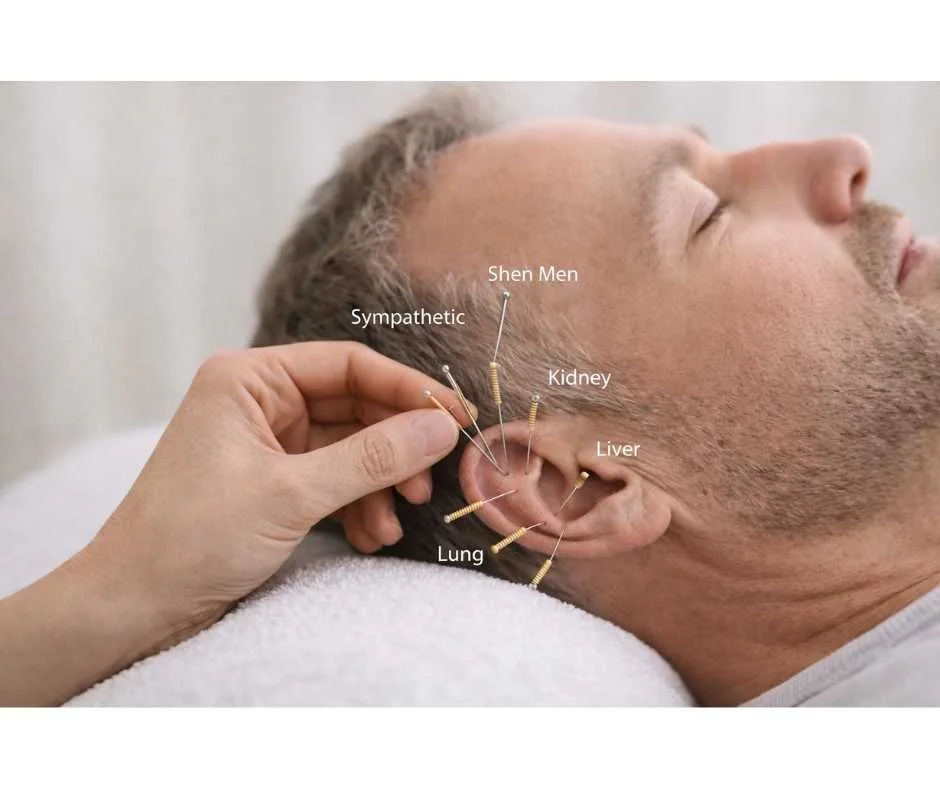
Acupuncture Points Commonly Used in Smoking Cessation Care
Treatment is individualized, but smoking cessation protocols often include a focused combination of body and auricular (ear) points chosen to regulate stress, cravings, and habit pathways.
Commonly used points include (10):
Shenmen (ear): nervous system calming and emotional regulation
Sympathetic point (ear): stress response modulation
Lung points (ear): respiratory and detoxification associations
Liver point (ear): metabolic and detox support
Kidney point (ear): fear and stress stabilization
Four Gates (hands and feet): systemic calming and circulation
Tim Mee (wrist): traditionally associated with altered cigarette taste perception
Precision matters more than quantity. Most treatments use approximately 6–12 needles.
Why Smoking Cessation Requires Repeated Nervous System Repatterning
Acupuncture is dose-dependent. One session may reduce cravings temporarily, but lasting change requires repeated exposure to regulatory input.
A common clinical approach includes:
Weekly sessions for 4–6 weeks
Gradual spacing as stability improves
Factors influencing treatment duration include:
Length of smoking history
Stress load and sleep quality
Prior quit attempts
Coexisting anxiety or chronic stress patterns
Long-term success improves when the nervous system is supported consistently rather than episodically (11).
Why Relapse Is Common—and How Acupuncture Helps Prevent It
Relapse often occurs not because cravings return, but because stress tolerance collapses. When the nervous system is overloaded, old coping strategies resurface automatically.
By improving baseline regulation, acupuncture:
Reduces stress-driven impulsivity
Improves emotional buffering
Increases pause between urge and action
Supports long-term pattern change
This is why acupuncture can be particularly helpful for individuals who repeatedly relapse despite strong motivation.
Safety and Side Effects
Acupuncture is generally safe when performed by a licensed practitioner. Side effects are uncommon and usually mild, such as temporary soreness, fatigue, or lightheadedness.
Most people experience relaxation, mental clarity, or a calm, grounded state after treatment (12).
A Systems-Based Approach to Smoking Cessation in Denver
At Denver Sports and Holistic Medicine, smoking cessation is approached through a systems-based lens that recognizes the role of stress physiology, habit loops, and nervous system regulation in addiction patterns.
Acupuncture may be combined with broader support strategies when appropriate to improve resilience and long-term outcomes.
→ Functional & Integrative Medicine
You may request a free 15-minute consultation with Dr. Martina Sturm to review your health concerns and outline appropriate next steps within a root-cause, systems-based framework.
Frequently Asked Questions About Acupuncture for Smoking Cessation
Does acupuncture actually help people quit smoking?
Acupuncture can support smoking cessation by reducing nicotine cravings, calming stress-related urges, and stabilizing nervous system activity during withdrawal. Rather than replacing nicotine, acupuncture works by helping the body regulate stress, mood, and reward signaling, which are common drivers of relapse. Results vary by individual, but many people report improved craving control and emotional steadiness when treatments are done consistently.
How does acupuncture reduce nicotine cravings?
Nicotine alters dopamine and stress-response pathways in the brain. Acupuncture influences these same systems by modulating autonomic nervous system activity and neurochemical signaling. This can reduce the intensity and frequency of cravings, particularly those triggered by stress, emotional discomfort, or habitual cues.
How long does it take for acupuncture to start working for smoking cessation?
Some people notice changes in cravings or stress levels after the first session, while others require several treatments before effects become noticeable. Smoking is a long-standing physiological and behavioral pattern, so improvement is typically progressive rather than immediate. Consistency over several weeks is usually necessary for more durable results.
Can acupuncture help if I’ve tried quitting many times before?
Yes. Many individuals who seek acupuncture for smoking cessation have already tried nicotine replacement, medications, or willpower-based approaches without lasting success. Acupuncture may be particularly helpful when relapse is driven by stress, anxiety, emotional regulation challenges, or nervous system dysregulation rather than purely chemical dependence.
Is acupuncture used alone or with other smoking cessation strategies?
Acupuncture can be used on its own or alongside other supportive strategies, depending on individual needs. Some people use it as their primary method, while others integrate it with lifestyle changes, stress management, or broader health support. Treatment plans are typically individualized rather than one-size-fits-all.
How many acupuncture sessions are usually needed to quit smoking?
There is no universal number of sessions. Many people begin with weekly treatments for several weeks, followed by less frequent maintenance visits. Factors such as smoking history, stress load, prior quit attempts, and overall health influence how long treatment is needed.
Does acupuncture help with withdrawal symptoms like anxiety or irritability?
Yes. Acupuncture is commonly used to calm the nervous system and reduce symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, restlessness, and sleep disruption. These symptoms are often more challenging than cravings themselves and play a major role in relapse.
Is acupuncture safe while quitting smoking?
Acupuncture is generally considered safe when performed by a licensed practitioner. Side effects are uncommon and usually mild, such as temporary soreness or fatigue. Many people feel relaxed or calm after treatment, which can be especially beneficial during the quitting process.
What if I’m not ready to quit completely yet?
Some individuals begin acupuncture while reducing smoking rather than stopping abruptly. Acupuncture may help lower cigarette consumption, reduce reliance on smoking for stress relief, and increase readiness to quit fully over time.
Still Have Questions?
If the topics above reflect ongoing symptoms or unanswered concerns, a brief conversation can help clarify whether a root-cause approach is appropriate.
Resources
World Health Organization – WHO traditional medicine strategy and acupuncture mechanisms
National Institute on Drug Abuse – Nicotine addiction and neurobiology
Journal of Neuroscience – Dopamine and serotonin adaptations in nicotine dependence
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health – Acupuncture overview
Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine – Neurochemical effects of acupuncture
Neuroscience Letters – Acupuncture and autonomic nervous system regulation
Addiction Biology – Stress, habit formation, and nicotine relapse
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews – Acupuncture for smoking cessation
Brain Research – Acupuncture modulation of dopamine signaling
Psychoneuroendocrinology – Stress reduction effects of acupuncture
Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment – Sensory changes during acupuncture-assisted cessation
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine – Acupuncture and detoxification pathways
Medical Acupuncture – Auricular acupuncture protocols for addiction
Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine – Long-term outcomes in acupuncture-supported cessation
Addictive Behaviors – Time course of craving reduction during smoking cessation
British Medical Journal – Safety profile of acupuncture