Leaky Gut Syndrome – How to Restore Your Health From the Inside Out
Understanding Intestinal Permeability, Inflammation, and the Root Causes of Chronic Symptoms
Leaky gut syndrome—clinically referred to as increased intestinal permeability—is a systems-level condition, not simply a digestive disorder. While it originates in the gastrointestinal tract, its effects often extend far beyond digestion. Many individuals with leaky gut do not initially report classic gut symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, or abdominal pain.
Instead, early signs frequently present as chronic fatigue, joint or muscle pain, inflammatory skin conditions, allergies, metabolic dysfunction, brain fog, or autoimmune flares. These seemingly unrelated symptoms reflect the gut’s central role in immune regulation, inflammatory signaling, and metabolic control.
From a functional medicine perspective, this pattern is well recognized. When the intestinal barrier becomes compromised, larger food particles, microbial fragments, and toxins can cross into circulation, triggering immune activation and systemic inflammation. Over time, this dysregulation can strain multiple organ systems—often manifesting far from the digestive tract and long before gastrointestinal symptoms become obvious.
This article explains what leaky gut is, how intestinal permeability develops, why symptoms often appear outside the digestive system, and which root-cause drivers—such as gluten exposure, inflammation, microbiome imbalance, immune activation, and environmental stressors—must be addressed to restore gut barrier integrity and whole-body health.
What Is Leaky Gut Syndrome?
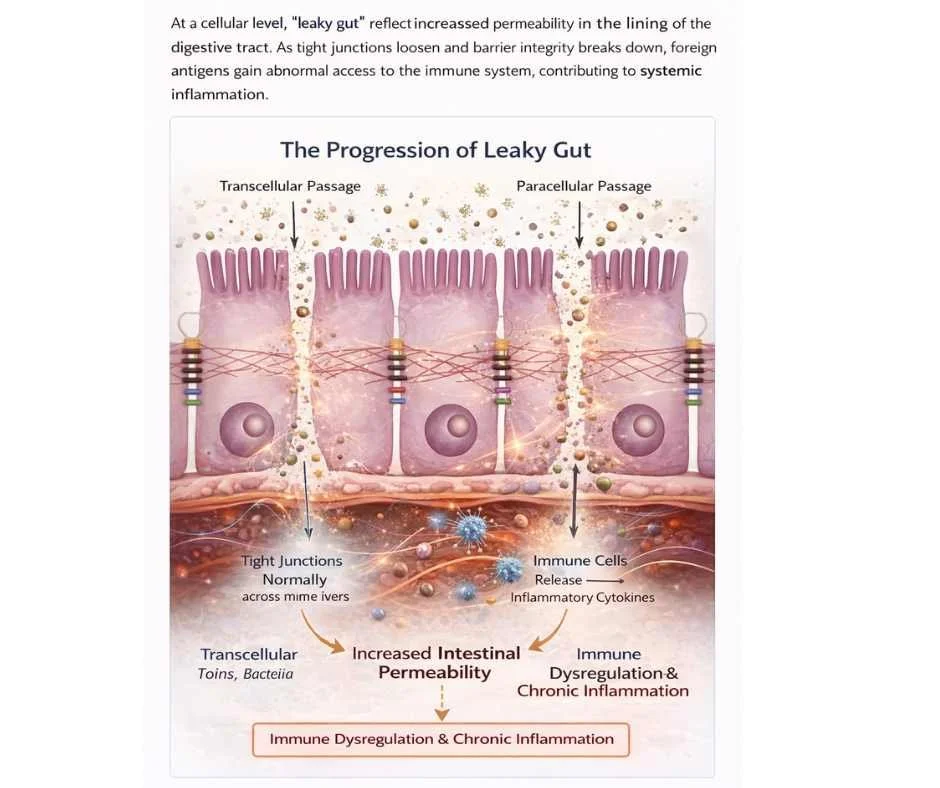
Leaky gut syndrome—clinically described as increased intestinal permeability—occurs when the intestinal barrier loses its ability to precisely regulate what passes from the gut into the bloodstream. Under healthy conditions, the gut lining functions as a selective interface, allowing the absorption of nutrients while preventing bacteria, endotoxins, and incompletely digested food particles from entering circulation.
This barrier is not a single structure, but a complex, multi-layered defense system composed of intestinal epithelial cells, mucus layers, immune signaling molecules, and the gut microbiome. Central to this system are tight junctions—specialized protein complexes that bind adjacent intestinal cells together and dynamically regulate permeability in response to diet, immune signals, microbial activity, and stress (1).
When tight junction integrity is disrupted, permeability increases. This allows larger particles—such as bacterial fragments (including lipopolysaccharides), food antigens, and environmental toxins—to cross the intestinal lining and enter systemic circulation. This process is sometimes described as “leakiness,” but clinically it represents a loss of barrier regulation, not structural damage alone.
Once these particles enter circulation, the immune system identifies them as foreign. Acute immune activation is a normal protective response; however, repeated or ongoing exposure leads to chronic immune stimulation, low-grade systemic inflammation, and progressive immune dysregulation. Over time, this can impair immune tolerance—the ability of the immune system to distinguish harmless substances from true threats—a pattern strongly associated with autoimmune conditions, chronic inflammatory disease, and food sensitivities (1,2).
Importantly, leaky gut is not a standalone diagnosis, but a foundational mechanism that contributes to a wide range of chronic health conditions. Its clinical relevance lies not in the term itself, but in understanding why barrier dysfunction develops, which systems are involved, and how intestinal permeability perpetuates whole-body inflammation.
How Increased Intestinal Permeability Develops at the Cellular Level
Why Leaky Gut Causes Symptoms Throughout the Body
Approximately 70% of the immune system is associated with the gut, making intestinal barrier integrity central to immune regulation and systemic inflammatory control (2). The gut is not only a digestive organ—it functions as a primary immune interface, continuously sampling what enters the body and determining whether tolerance or defense is required.
When intestinal permeability increases, this regulatory role becomes disrupted. Larger immune-activating particles such as bacterial fragments, endotoxins, and food antigens gain access to circulation, triggering immune signaling far beyond the gut itself. As this exposure persists, several downstream effects can occur:
Inflammatory signaling spreads systemically, shifting the immune system toward chronic low-grade activation
Immune tolerance is impaired, increasing sensitivity to foods, environmental triggers, and self-tissues
Autoimmune activity becomes more likely as regulatory immune pathways are strained
Metabolic and hormonal signaling is affected, as inflammation interferes with insulin sensitivity, thyroid conversion, adrenal regulation, and mitochondrial energy production
Because these effects involve multiple regulatory systems, symptoms often appear in tissues seemingly unrelated to digestion. Joint and muscle pain, respiratory or allergy-type symptoms, inflammatory skin conditions, fatigue, mood or cognitive changes, and immune dysregulation may all reflect gut-driven immune activation—even when gastrointestinal symptoms are mild or absent.
This systemic pattern is one reason leaky gut is frequently overlooked in conventional care: symptoms are evaluated in isolation rather than traced back to a shared regulatory source.
Key Factors That Contribute to Leaky Gut Syndrome
Leaky gut rarely develops from a single insult. Instead, increased intestinal permeability reflects cumulative and often overlapping stressors that impair gut barrier regulation over time (1–4). These stressors can weaken tight junction integrity, disrupt immune signaling, alter microbiome balance, and reduce the gut’s ability to repair itself.
Common contributors include:
Genetic susceptibility, particularly in individuals with autoimmune predisposition, where immune tolerance mechanisms are already more vulnerable
Inflammatory dietary exposures, including gluten, ultra-processed foods, refined sugars, industrial seed oils, and food additives that promote gut inflammation and tight junction disruption
Medications such as NSAIDs, antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, and hormonal contraceptives, which can damage the gut lining directly or alter microbial balance and immune signaling
Environmental toxins, including pesticides, glyphosate, mold byproducts, and air pollution, which increase oxidative stress and inflammatory burden at the gut–immune interface
Chronic psychological or physiological stress, which alters cortisol and autonomic signaling, reduces gut blood flow, and increases permeability
Gut microbiome imbalances, including bacterial dysbiosis and fungal overgrowth, which impair short-chain fatty acid production and compromise epithelial repair
Low vitamin D status, which weakens immune regulation, reduces antimicrobial defense, and impairs epithelial barrier integrity (3,4)
In most individuals, multiple factors are active simultaneously, compounding barrier dysfunction and sustaining immune activation. For this reason, identifying which contributors are present—and how they interact—is critical. Addressing only one factor while others remain unresolved often leads to incomplete healing or symptom recurrence.
Effective leaky gut care depends not on eliminating every possible trigger, but on prioritizing the drivers most responsible for ongoing barrier disruption.
The Progression of Leaky Gut and Autoimmune Risk
In many individuals, increased intestinal permeability is associated with a recognizable pattern of immune escalation rather than an abrupt onset of autoimmune disease. This progression reflects the gradual loss of immune tolerance as the gut–immune interface becomes increasingly dysregulated.
1. Food Sensitivities and Immune Sensitization
Early immune activation often presents as delayed, non–IgE-mediated food reactions. These responses reflect immune sensitization to food antigens that cross the intestinal barrier due to increased permeability. Symptoms may be subtle at first—fatigue, joint stiffness, headaches, skin flares, or digestive discomfort—and are frequently dismissed or misattributed.
2. Environmental and Chemical Sensitivities
As barrier dysfunction and immune activation persist, the threshold for immune reactivity may lower. Sensitivity to chemicals, fragrances, molds, pollutants, and other environmental exposures becomes more common, reflecting broader immune dysregulation and impaired detoxification signaling.
3. Autoimmune Activation
With sustained antigen exposure and chronic immune stimulation, immune regulation may break down further. In genetically susceptible individuals, this can contribute to loss of self-tolerance, increasing the risk of autoimmune disease—defined by immune-mediated attack on the body’s own tissues (5).
This progression is not inevitable, but it underscores why early identification and targeted intervention matter. Addressing intestinal permeability and its drivers before immune tolerance is significantly impaired may reduce the likelihood of downstream autoimmune and inflammatory disease.
Healing Leaky Gut: A Functional Medicine Approach
Healing leaky gut involves more than reducing symptoms—it requires restoring intestinal barrier function, recalibrating immune signaling, and removing the upstream factors that continue to disrupt permeability. From a functional medicine perspective, intestinal healing is not a single intervention, but a sequenced, systems-based process guided by individual physiology.
Rather than suppressing immune responses or masking inflammation, functional medicine focuses on identifying why barrier dysfunction developed in the first place and addressing those drivers in the correct order.
Support strategies may include:
Personalized nutrition, designed to reduce inflammatory load, remove immune-reactive foods, and support epithelial repair while maintaining adequate nutrient intake
Targeted gut-repair nutrients and microbiome support, selected based on barrier integrity, microbial balance, immune activity, and tolerance capacity rather than generic supplementation
Removal of dietary, medication-related, and environmental triggers that continue to impair tight junction regulation or provoke immune activation
Stress and nervous system regulation, recognizing that autonomic imbalance and chronic cortisol signaling directly influence gut permeability, immune tone, and tissue repair
Support for detoxification and immune balance, particularly when toxin exposure, oxidative stress, or inflammatory burden is contributing to ongoing barrier disruption
In some cases, herbal therapies and acupuncture may be used adjunctively to support immune regulation, inflammatory balance, and nervous system tone when clinically appropriate and properly sequenced (6–8).
Importantly, effective healing does not require addressing every possible factor at once. Progress is best achieved by prioritizing the mechanisms most responsible for ongoing permeability, monitoring response, and adjusting care as regulation improves.
Why a Personalized, Systems-Based Approach Is Often Necessary
Leaky gut does not develop from a single cause, and it does not resolve with a one-size-fits-all protocol. Intestinal permeability is the downstream result of multiple interacting stressors that vary significantly from person to person.
These may include gluten or food antigen exposure, microbiome imbalance, chronic infections, immune dysregulation, toxin burden, metabolic instability, hormonal signaling disruption, nervous system stress, or impaired detoxification capacity. In many cases, several of these factors are present simultaneously—each amplifying the others.
Because the intestinal barrier sits at the intersection of the immune system, endocrine signaling, and metabolic regulation, effective healing requires identifying which drivers are active in a given individual and addressing them in the correct sequence. Applying generalized diets, supplements, or “gut healing” protocols without this context often leads to partial improvement, symptom relapse, or stalled progress.
A personalized, systems-based approach focuses on pattern recognition rather than symptom matching, allowing care to be tailored to the specific mechanisms disrupting gut barrier integrity. This precision is what supports durable healing—not temporary symptom control.
Personalized Gut Health Support
Chronic inflammation, autoimmune symptoms, fatigue, and persistent, unexplained health concerns are often evaluated in isolation. When gut barrier dysfunction and immune dysregulation are contributing factors, symptom-focused care alone is rarely sufficient.
At Denver Sports & Holistic Medicine, care is grounded in a root-cause, systems-based framework. Evaluation focuses on identifying the specific drivers of intestinal permeability and immune activation—such as dietary triggers, microbiome imbalance, inflammatory burden, stress physiology, or environmental exposures—and addressing them through an individualized plan designed to support durable healing rather than short-term symptom control.
→ Gut Health & Digestive Restoration
You may request a free 15-minute consultation with Dr. Martina Sturm to review your health concerns and outline appropriate next steps within a root-cause, systems-based framework.
Frequently Asked Questions About Leaky Gut Syndrome
What is leaky gut syndrome?
Leaky gut syndrome refers to increased intestinal permeability, a state in which the gut lining becomes compromised and allows inflammatory substances to cross into the bloodstream. This can trigger immune activation and contribute to systemic inflammation rather than isolated digestive symptoms.
Is leaky gut a real medical condition?
While “leaky gut syndrome” is not always used as a formal diagnosis in conventional medicine, intestinal permeability is a well-documented physiological phenomenon supported by extensive research. Functional medicine uses this framework to explain how gut barrier dysfunction contributes to chronic disease.
Can you have leaky gut without digestive symptoms?
Yes. Many people with leaky gut experience joint pain, fatigue, skin issues, allergies, metabolic dysfunction, or autoimmune flares without significant digestive complaints. Because the gut plays a central role in immune regulation, symptoms often appear outside the digestive tract.
What causes leaky gut syndrome?
Leaky gut typically develops from multiple overlapping factors, including inflammatory foods, medications, chronic stress, environmental toxins, gut microbiome imbalances, infections, and nutrient deficiencies. It is rarely caused by a single trigger.
Is leaky gut linked to autoimmune disease?
Increased intestinal permeability is strongly associated with immune dysregulation and autoimmune disease development. When the gut barrier is compromised, immune tolerance can break down, increasing the risk of autoimmune activity in genetically or environmentally susceptible individuals.
How is leaky gut different from food allergies?
Food allergies are typically IgE-mediated reactions that cause immediate symptoms. Leaky gut involves delayed immune activation driven by increased permeability, which can lead to food sensitivities and systemic inflammation rather than acute allergic responses.
Can leaky gut be healed?
Yes. The gut lining is capable of repair when contributing factors are addressed. Healing focuses on reducing inflammatory triggers, restoring gut barrier integrity, calming immune activation, and supporting the microbiome, often through a personalized, stepwise approach.
How long does it take to heal leaky gut?
Healing timelines vary depending on the severity of gut disruption, underlying health conditions, and consistency of care. Some people notice improvement within weeks, while others require several months of targeted support for durable healing.
Do probiotics help with leaky gut?
Probiotics may be helpful for some individuals, but they are not a standalone solution. Gut repair often requires addressing diet, stress, immune activation, and environmental factors alongside targeted microbiome support.
When should someone seek professional support for leaky gut?
Professional guidance can be helpful when symptoms are persistent, systemic, worsening, or associated with autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. A personalized approach helps clarify root causes and appropriate next steps, rather than relying on trial-and-error alone.
Still Have Questions?
If the topics above reflect ongoing symptoms or unanswered concerns, a brief conversation can help clarify whether a root-cause approach is appropriate.
Resources
Nutrients – Leaky gut syndrome and nutritional compounds that support intestinal barrier integrity
Trends in Food Science & Technology – Pathogenesis of celiac disease and other gluten-related disorders and mitigation strategies
Nature Reviews Immunology – Vitamin D and the immune system
Gut – Intestinal barrier function and its regulation by the immune system
Nature Reviews Rheumatology – Environmental triggers of autoimmune disease
Frontiers in Immunology – Herbal medicines and their role in immune modulation
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology – Gut microbiota and immune system interactions
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine – Effects of acupuncture on immune and inflammatory markers