Gut health influences digestion, immune regulation, inflammation, hormone metabolism, and metabolic resilience. This in-depth guide explains how intestinal barrier function, the microbiome, and digestive capacity interact to shape whole-body health—and why gut dysfunction often drives chronic symptoms beyond the digestive tract.
Read MoreAlcohol is deeply normalized in modern culture, yet from a biological standpoint it functions as a systemic toxin. This in-depth article explores how alcohol impacts detoxification pathways, nutrient reserves, gut health, sleep quality, and nervous system regulation—and why individual biology determines risk long before conventional disease markers appear.
Read MoreCAFO-raised meat, lab-grown food technologies, and insect-derived ingredients are increasingly common—but rarely transparent. Part 3 of this food toxin series explores how industrial meat production and emerging food alternatives may impact hormones, gut health, immunity, and long-term metabolic resilience.
Read MoreGluten can contribute to intestinal permeability by disrupting the gut barrier and triggering immune activation. Learn the signs of gluten-related leaky gut and how to support healing at the root cause.
Read MoreMany people experience persistent symptoms after eating gluten despite negative celiac testing. This article explains what non-celiac gluten sensitivity is, how it affects the gut and immune system, and how it can be identified and managed within a root-cause framework.
Read MoreThyroid hormones rely on gut integrity, immune regulation, and proper nutrient absorption to function at the cellular level. This article explains why thyroid symptoms often persist despite normal labs—and how gut health shapes thyroid regulation.
Read MoreHashimoto’s disease is not simply a thyroid problem—it is a progressive autoimmune condition shaped by immune dysfunction, gut health, environmental exposures, and stress physiology. This guide explains why symptoms often appear long before thyroid labs change and how a root-cause, systems-based approach reframes long-term care.
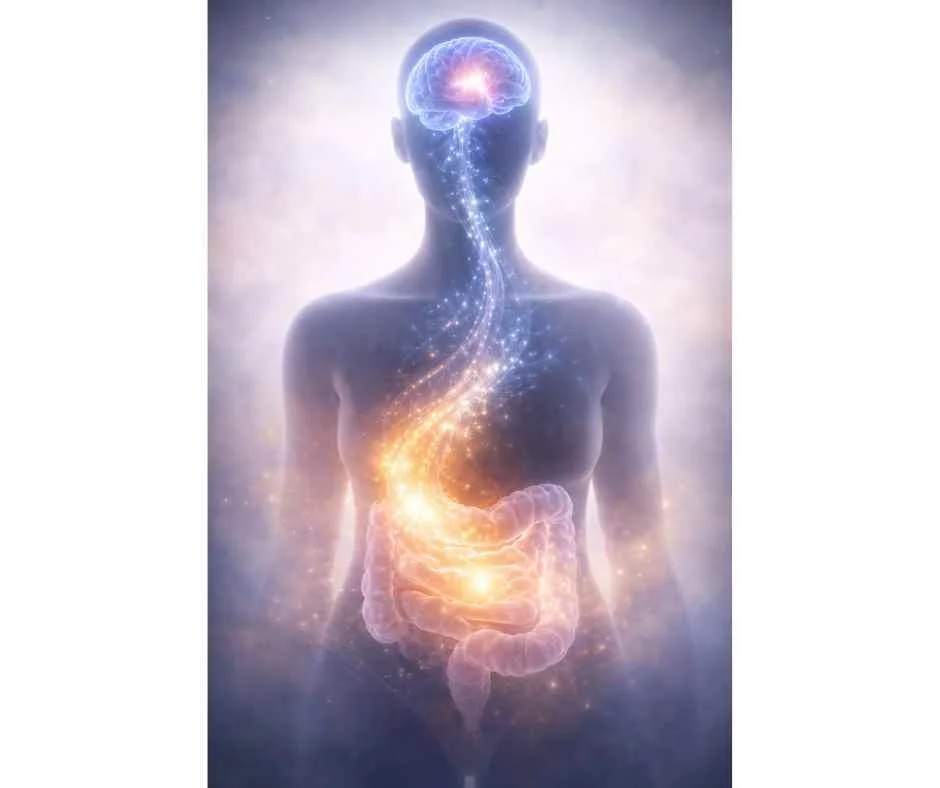
Read MoreThe gut–brain connection describes the constant communication between the digestive system and the nervous system that shapes digestion, inflammation, stress response, mood, and cognitive function. Disruptions in gut health can influence far more than digestion alone—helping explain why symptoms such as anxiety, fatigue, brain fog, and chronic inflammation often overlap.
Read MoreLeaky gut syndrome—also known as increased intestinal permeability—can drive inflammation, immune dysfunction, and chronic symptoms throughout the body. Learn how to heal at the root cause.
Read MoreAcid reflux is not always caused by excess stomach acid. Discover how low stomach acid, LES dysfunction, medications, stress, and diet contribute to GERD—and how a root-cause, natural treatment approach can restore digestive balance.
Read More